- 麦克风权限:Privacy – Microphone Usage Description 是否允许此App使用你的麦克风?
- 相机权限: Privacy – Camera Usage Description 是否允许此App使用你的相机?
- 相册权限: Privacy – Photo Library Usage Description 是否允许此App访问你的媒体资料库?
- 通讯录权限: Privacy – Contacts Usage Description 是否允许此App访问你的通讯录?
- 蓝牙权限:Privacy – Bluetooth Peripheral Usage Description 是否许允此App使用蓝牙?
- 语音转文字权限:Privacy – Speech Recognition Usage Description 是否允许此App使用语音识别?
- 日历权限:Privacy – Calendars Usage Description
- 定位权限:Privacy – Location When In Use Usage Description
- 定位权限: Privacy – Location Always Usage Description
- 位置权限:Privacy – Location Usage Description
- 媒体库权限:Privacy – Media Library Usage Description
- 健康分享权限:Privacy – Health Share Usage Description
- 健康更新权限:Privacy – Health Update Usage Description
- 运动使用权限:Privacy – Motion Usage Description
- 音乐权限:Privacy – Music Usage Description
- 提醒使用权限:Privacy – Reminders Usage Description
- Siri使用权限:Privacy – Siri Usage Description
- 电视供应商使用权限:Privacy – TV Provider Usage Description
- 视频用户账号使用权限:Privacy – Video Subscriber Account Usage Description
iOS:UITextField中文输入法输入时对字符长度的限制
如题的问题,又是个让我抓狂了大半天的问题,还是做个记录,有与类似问题的同学可参考,但不一定对。具体问题还需具体分析。我遇到的需求是这样的:有一个输入框,输入框内输入文字,文字字数限制在20字。
我采用了UITextField作为我的输入框控件,并且在委托方法:
![]()

中实现了对字符串的长度限制,实现如下:
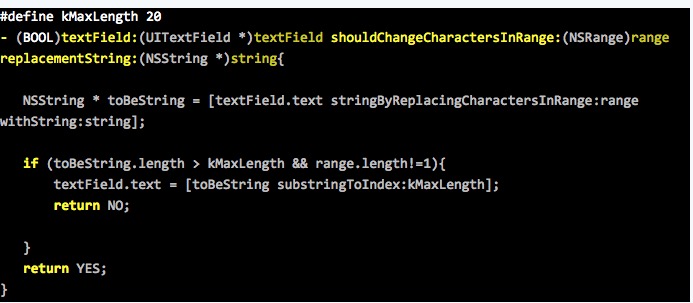

这样实现的结果是:对于纯字符的统计没有什么问题,当输入的字符超过限制时输入框便截取*大限制长度的字符串。但是,有个问题,当使用拼音输入法时,该委托方法中的*后一个参数string接受的是输入的字母,而不是选择的汉字,造成的结果是,当想输入文字“我在编程”,输入拼音“wozaibiancheng”,每输入一个字母便会进入委托方法,统计的字符长度是字母的长度,实际上汉字还未超过限制长度,但是字母的长度超过了导致无法继续输入。
而且,致命的是,这个委托方法并不响应,选中候选汉字的过程,这就没有办法重新修正字符长度的统计了。
网上查了一些方法,有个叫Onyx的博主写了篇文章:iOS中UITextView/UITextField 输入英文和拼音状态下如何正确的统计输入的文字字数 看起来似乎是和我同样的问题,但是当我把他的代码搬到我的类里时,实现的结果并不理想,我没有得到想要的结果,而且他的方法看起来似乎复杂了点,我也没有研究清楚这个方法的问题出在哪。之所以把他的这篇博文引进来,是因为他的文章后来给了我些启发。
我刚开始时候并没有发现

![]()
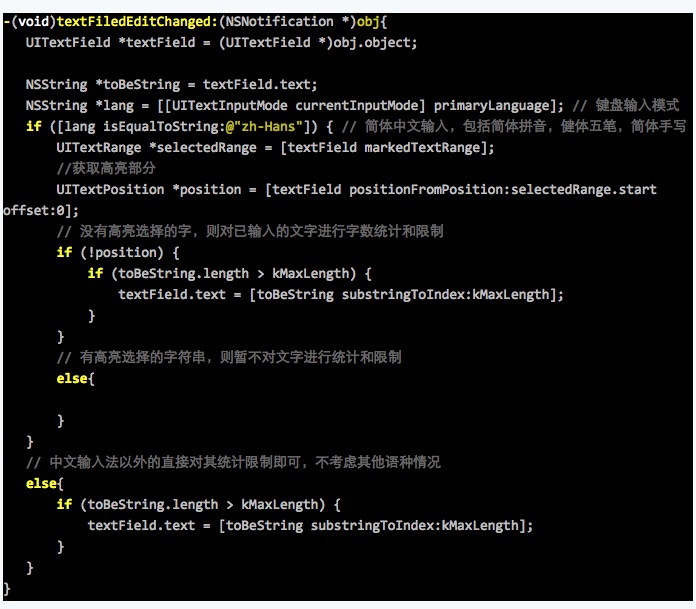
这个委托方法没有响应*后拼音到汉字的过程,当我发现这个问题时,问题便也差不多得到了解决。因为在之前向微博上的一个朋友咨询时,他告诉我可以注册这个观察者 UITextInputCurrentInputModeDidChangeNotification
在它的监听下可以得到中文。我刚开始时候理解错了他的意思,以为得到的就是*终选中的汉字,而中间输入的拼音并不会被得到。但其实这个监听,比以上的委托方法多了*后一步而已,即从拼音到中文的过程。
所以实现的代码如下。
<1>在init时候注册notification:
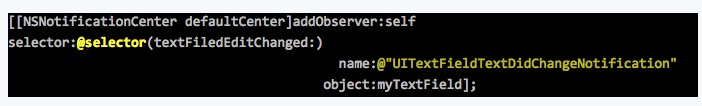
![]()
<2>实现监听方法:

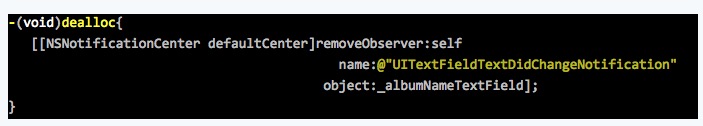
<3>在dealloc里注销掉监听方法,切记!

iOS开发-登录界面开发(4)AFNetworking的引入-Swfit4.1_Xcode9.3.1
1.AFNetworking是个啥?
网络请求开源框架, iOS和Mac OS都能用。
2.SwiftyJSON是个啥?
另一个开源框架,处理JSON数据(解析数据、生成数据)。
3.让我们来引入AFNetworking、SwiftyJSON:
3.1.找到你项目的地址:(顺便介绍一个快捷键,option+command+c,复制文件或者文件夹的路径)
/Users/jimi/Documents/iOS/Demo/Myy
3.2.打开终端,输入,回车:
cd /Users/jimi/Documents/iOS/Demo/Myy
3.3.创建一个 Podfile:
touch Podfile
3.4.你可以选择使用命令行编辑,比如:“vim Podfile”回车,开始编辑,按“i”,进行插入,插入下面的语句,按Esc,按:,按wq+回车,进行保存退出。
或者你可以,直接把下面的语句,复制到 Podfile 文件里:
# 设置支持*低平台 platform :ios, '8.0' target 'Myy' do # 如果是Swift项目,需添加"use_frameworks!" use_frameworks! # 如果要使用固定版本 可以像下面这么写 # pod 'AFNetworking', '~> 3.2.1' pod "AFNetworking" pod "SwiftyJSON" end
3.5.开始下载引入:
pod install
4.可以打开引入第三方框架的工程了,打开这个文件,就可以了:
/Users/jimi/Documents/iOS/Demo/Myy/Myy.xcworkspace
5.这样,我们就同时引入2个开源框架了。引入的是*新版本,如果你特殊需求,可以像注释写得一样,引入指定版本。
工作记录8:iOS 传值问题总结(7种传值完美介绍)
1、属性传值
前向后传值。
记住:
/*
1: 属性传值*步需要用到什么类型就定义什么样的属性
2: 从上一个页面到一个页面的选中方法里面将要传的值传到来(上一个页面)备注:这种方法只适用于上一个页面推到下一个页面
*/
MainViewController与SecondViewController两个视图 控制器 ,点击MainViewController中的按钮将跳转到SecondViewController视图,同时想要传递一个值过去。这时可以利用属性传值。
首先SecondViewController视图中需要有一个属性用来 存储 传递过来的值:
@property(nonatomic,retain) NSString *firstValue ;//属性传值
然后MainViewController视图需要引用SecondViewController视图的头文件,在视图中的按钮点击事件中,通过SecondViewController的对象将需要传递的值存在firstValue中:
(void)buttonAction:(UIButton *)button
{
SecondViewController *second =
[[SecondViewController alloc]init];//用下一个视图的属性接受想要传过去的值,属性传值
second.firstValue = _txtFiled.text;
[self.navigationController pushViewController:second animated:YES];
}
页面跳转之后,就能在SecondViewController视图中,通过存值的属性,取用刚才传递过来的值:
//显示传过来的值[_txtFiled setText:_firstValue];//firstValue保存传过来的值2、方法传值:
需求同一中的 属性传值 一样,但是要通过使用方法传值,可以直接将方法与初始化方法合并,此时当触发MainViewController的按钮点击事件并跳转到 SecondViewController时,在按钮点击事件中可以直接通过SecondViewController的初始化,将值保存在 firstValue中:
初始化方法如下: 首先SecondViewController视图中需要有一个属性用来 存储 传递过来的值:
@property(nonatomic,retain) NSString *firstValue ;//传值用
//重写初始化方法,用于传值
- (id)initWithValue:(NSString *)value
{
if(self = [super initWithNibName:nil bundle:nil]) { self.firstValue = value;
}
return self;}
方法传值:
- (void)buttonAction:(UIButton *)button
{//将方法传值与初始化写到一起
SecondViewController *second = [[SecondViewController alloc]
initWithValue:_txtFiled.text];//此时已经将值存在firstValue中
[self.navigationController pushViewController:second animated:YES];
}
这样就可以直接通过firstValue属性获得传递过来的值:
//显示传过来的值[_txtFiled setText:_firstValue];//firstValue保存传过来的值3、协议传值 代替协议代理传值,主要时间点问题。
上面 中说明了如何从A传值到B,这次要讲的是如何从A进入B,在B输入值后回传给A,这类似于Android中的利用 Activity的onActivityResult回调方法实现两个Activity之间的值传递,那么在IOS中如何实现这个功能呢,答案是使用 Delegate(委托协议)。
工程结构如下:
其中有两个ViewController分别对应两个界面,一个协议PassValueDelegate用来实现传值协议,UserEntity是传递数据的对象。
以下是实现的效果:点击Open进入Second界面,输入完毕点击OK后回到First界面并显示结果
协议中声明的方法:
- #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
- @ class UserEntity;
- @protocol PassValueDelegate <NSObject>
- -( void )passValue:(UserEntity *)value;
- @end
- 在*个窗口实现协议:
- #import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
- #import “PassValueDelegate.h”
- //*个窗口遵守PassValueDelegate
- @interface ViewController : UIViewController<PassValueDelegate>
- @property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *nameLabel;
- @property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *ageLabel;
- @property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *gendarLabel;
- – (IBAction)openBtnClicked:(id)sender;
- @end
.m文件中实现协议的方法:
[cpp]view plaincopy
- //实现协议,在*个窗口显示在第二个窗口输入的值方法
- -( void )passValue:(UserEntity *)value
- {
- self.nameLabel.text = value.userName;
- self.ageLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@ “%d” ,value.age];
- self.gendarLabel.text = value.gendar;
- }
点击Open按钮所触发的事件:
[cpp]view plaincopy
- //点击进入第二个窗口的方法
- – (IBAction)openBtnClicked:(id)sender {
- SecondViewController *secondView = [[SecondViewController alloc] initWithNibName:@ “SecondViewController” bundle:[NSBundle mainBundle]];
- //设置第二个窗口中的delegate为*个窗口的self
- secondView.delegate = self;
- [self.navigationController pushViewController:secondView animated:YES];
- }
第二个窗口中声明一个NSObject对象,该对象遵守PassValueDelegate协议:
[cpp]view plaincopy
- #import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
- #import “PassValueDelegate.h”
- @interface SecondViewController : UIViewController
- @property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *nameTextField;
- @property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *ageTextFiled;
- @property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *gendarTextField;
- //这里用assign而不用retain是为了防止引起循环引用。
- @property(nonatomic,assign) NSObject<PassValueDelegate> *delegate;
- – (IBAction)okBtnClicked:(id)sender;
- – (IBAction)closeKeyboard:(id)sender;
- @end
输入完毕后,点击OK按钮所触发的事件:
[cpp]view plaincopy
- – (IBAction)okBtnClicked:(id)sender {
- UserEntity *userEntity = [[UserEntity alloc] init];
- userEntity.userName = self.nameTextField.text;
- userEntity.gendar = self.gendarTextField.text;
- userEntity.age = [self.ageTextFiled.text intValue];
- //通过委托协议传值
- [self.delegate passValue:userEntity];
- //退回到*个窗口
- [self.navigationController popViewControllerAnimated:YES];
- [userEntity release];
- }
以上就实现了使用Delegate在两个ViewController之间传值,这种场景一般应用在进入子界面输入信息,完后要把输入的信息回传给前一个界面的情况,比如修改用户个人信息,点击修改进入修改界面,修改完后到显示界面显示修改后的结果。
4、Block传值 //参考 http://liuyafang.blog.51cto.com/8837978/1551399
1.*页中 声明一个 block, 需要传入一个颜色 , 让当前的 view 变色
// 声明一个 block, 需要传入一个颜色 , 让当前的 view 变色
void (^changeColor)( UIColor *color) = ^( UIColor *color){
self . view . backgroundColor = color;
};
2 . *页中 //block 传值 ——— 将 block 给第二个页面
SecondViewController *secondVC = [[ SecondViewController alloc ] init ];
//block 传值 ——— 将 block 给第二个页面
secondVC. block = changeColor;
3.第二页中定义 — 当 block 变量作为一个类的属性 , 必须要使用 copy 修饰
//block 传值 ——— 将 block 给第二个页面
//block 传值 — 当 block 变量作为一个类的属性 , 必须要使用 copy 修饰
@property ( nonatomic , copy ) void (^block)( UIColor *color);
4.在第二页中给block传值
//block 传值 ——— 将传值给 block
NSArray *array = [ NSArray arrayWithObjects :[ UIColor yellowColor ], [ UIColor cyanColor ], [ UIColor greenColor ], [ UIColor brownColor ], nil ];
self . block ([array objectAtIndex : rand () % 4 ]);
类和文件
AppDelegate.m
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
|
MainViewController.m
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
|
|
SecondViewController.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
|
SecondViewController.m
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
|
5 单例 传值
单例只会对某个类实例化一次/单例类,对单例这个类实例化一次有且仅有一个对象
你单例初始化,只能初始化一次,然后你指向的对象,其实都是指向一个内存地址,也就是同一块内存,所以都是一样的/
那么,只能有一个对象,就是实例化的那个
(1)定义单例类singleton .h文件
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface singleton : NSObject //步骤一
//@property (strong,nonatomic) UITextField *value;//*开始的时候把这个value定义为UITextField了,然后在init里面又没有初始化它,就取不到值。任何对象都要初始化它才能使用。
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *value;
//+(id)shareData:
+(singleton *)shareData; //步骤二
@end
//.m文件
#import “singleton.h”
@implementation singleton
static singleton *singletonData = nil; //步骤三
+(singleton *)shareData { //步骤四
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
singletonData = [[singleton alloc] init];
});
return singletonData;
}
-(id)init { //步骤五
if (self = [super init]) {
// self.value = [[UITextField alloc]init];
}
return self;
}
@end
//以上是一个完整单例子
(2)ViewController
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import “OneViewController.h”
#import “singleton.h” //引用单例
@interface ViewController : UIViewController
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *qqTextfield;
– (IBAction)go:(id)sender;
@end
– (IBAction)go:(id)sender {
//单例的使用
singleton *oneS = [singleton shareData];
// oneS.value.text = self.qqTextfield.text;
oneS.value = self.qqTextfield.text;
OneViewController *oneVC = [[OneViewController alloc]init];
[self presentViewController:oneVC animated:YES completion:nil];
}
(3)OneViewController
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import “singleton.h”
@interface OneViewController : UIViewController
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *oneTextField;
@end
– (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view from its nib.
self.oneTextField.text = [singleton shareData].value;
}
6:数据共享。
OS app之间要共享数据不是那么容易,因为每个app都是sandbox。然后,有时候又不得不跟其它app之间共享数据,那应该怎么办呢?
下面是一些常用方法的总结:
-
UIDocumentInteractionController
Availability: iOS 3.2+
具体用法参见: http://mobile.tutsplus.com/tutorials/iphone/previewing-and-opening-documents-with-uidocumentinteractioncontroller/
- UIActivityViewController
Availability: iOS 6.0+ - Shared Keychain Access
这个要求app之间用的是同样的证书 - Custom URL Scheme
通过构造URL,把数据作为参数传递过去。 本地测试过,传递10000个字符都可以,不过不要太长,内存可能吃不消。 - Web Service 通过dropbox或者其他第三方的服务来共享数据。
- UIPasteboard + URL Scheme 通过URL scheme传递UIPasteboard的名称,然后通过UIPasteboard共享数据。
微信iOS SDK应该采用的就是这种方式。
不过在iOS 7上,这种方法会存在问题,如果采用这种方案,得赶紧想办法解决。
1) http://enharmonichq.com/sharing-data-locally-between-ios-apps/
2) http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17080074/ios7-beta-doesnt-allow-inter-app-communication-by-uipasteboard
7:通知传值
通知中心
NSNotificationCenter提供了一种更加解耦的方式。*典型的应用就是任何对象对可以发送通知到中心,同时任何对象可以监听中心的通知。
发送通知的代码如下:
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:@”myNotificationName” object:broadcasterObject];
注册接收通知的代码如下:
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:listenerObject selector:@selector(receivingMethodOnListener:) name:@”myNotificationName” object:nil];
注册通知的时候可以指定一个具体的广播者对象,但这不是必须的。你可能注意到了defaultCenter 。实际上这是你在应用中会使用到的唯一的中心。通知会向整个应用开放,因此只有一个中心。
同时还有一个NSDistributedNotificationCenter。这是用来应用间通信的。在整个计算机上只有一个该类型的中心。
优点: 通知的发送者和接受者都不需要知道对方。可以指定接收通知的具体方法。通知名可以是任何字符串。
缺点: 较键值观察需要多点代码。在删掉前必须移除监听者。 不能传大量数值,只能让谁去做什么事。
ios 取消键盘响应
在FormViewController中,则不需要在实现UITextFieldDelegate,来对处于编辑状态的textField进行跟踪,也不必担心将来会添加N个UITextView,只要是在FormViewController下,我们只要调用 [self.view endEditing:YES];就可以了
http://my.oschina.net/hmj/blog/100020
iOS中的几种定时器详解
在软件开发过程中,我们常常需要在某个时间后执行某个方法,或者是按照某个周期一直执行某个方法。在这个时候,我们就需要用到定时器。
然而,在iOS中有很多方法完成以上的任务,经过查阅资料,大概有三种方法:NSTimer、CADisplayLink、GCD。接下来我就一一介绍它们的用法。
一、NSTimer
1.创建方法
-
/**
-
类方法创建定时器对象
-
*
-
@property ti 之行之前等待的时间。比如设置为1.0,代表1秒后之行方法
-
@property aTarget 需要执行方法的对象
-
@property aSelector 需要执行的方法
-
@property userInfo 保存定时器使用者的一些信息
-
@property yesOrNo 是否需要循环
-
*
-
@return 返回定时器对象
-
*/
-
(NSTimer *)scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:(NSTimeInterval)ti
-
target:(id)target
-
selector:(SEL)aSelector
-
userInfo:(id)userInfo
-
repeats:(BOOL)repeats;
-
-
class func scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval(_ ti: NSTimeInterval,
-
target aTarget: AnyObject,
-
selector aSelector: Selector,
-
userInfo userInfo: AnyObject?,
-
repeats yesOrNo: Bool) -> NSTimer
2.释放方法
-
– (void)invalidate;
-
-
func invalidate()
- 注意:
调用创建方法后,target对象的计数器会加1,直到执行完毕,自动减1。如果是循环执行的话,就必须手动关闭,否则可以不执行释放方法。
3.特性
- 存在延迟:
不管是一次性的还是周期性的timer的实际触发事件的时间,都会与所加入的RunLoop和RunLoop Mode有关,如果此RunLoop正在执行一个连续性的运算,timer就会被延时出发。重复性的timer遇到这种情况,如果延迟超过了一个周期,则会在延时结束后立刻执行,并按照之前指定的周期继续执行。 - 必须加入Runloop:
使用上面的创建方式,会自动把timer加入MainRunloop的NSDefaultRunLoopMode中。如果使用以下方式创建定时器,就必须手动加入Runloop:
-
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:5 target:self selector:(timerAction) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
-
[[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
- UIScrollView 拖动时执行的是 UITrackingRunLoopMode,会导致暂停定时器,等恢复为 NSDefaultRunLoopMode 时才恢复定时器。所以如果需要定时器在 UIScrollView 拖动时也不影响的话,建议添加到 UITrackingRunLoopMode 或 NSRunLoopCommonModes 中:
二、CADisplayLink
1.创建方法
-
/**
-
* 类方法创建显示连接对象
-
*
-
* @property target 执行方法的对象
-
* @property sel 需要执行的方法
-
*
-
* @return 返回显示连接对象
-
*/
-
+ (CADisplayLink *)displayLinkWithTarget:(id)target
-
selector:(SEL)sel;
-
/**
-
* 调度显示连接器去发送通知
-
*
-
* @property runloop 运行循环
-
* @property mode 运行循环的模式
-
*
-
* @return 无
-
*/
-
– (void)addToRunLoop:(NSRunLoop *)runloop
-
forMode:(NSString *)mode;
-
-
init(target target: AnyObject,
-
selector sel: Selector)
-
func addToRunLoop(_ runloop: NSRunLoop,
-
forMode mode: String)
2.停止方法
-
/* 当把CADisplayLink对象add到runloop中后,selector就能被周期性调用,
-
类似于重复的NSTimer被启动了;执行invalidate操作时,CADisplayLink对
-
象就会从runloop中移除,selector调用也随即停止,类似于NSTimer的invalidate
-
方法。*/
-
– (void)invalidate;
-
-
func invalidate()
3.特性
- 屏幕刷新时调用:
CADisplayLink是一个能让我们以和屏幕刷新率同步的频率将特定的内容画到屏幕上的定时器类。CADisplayLink以特定模式注册到runloop后,每当屏幕显示内容刷新结束的时候,runloop就会向CADisplayLink指定的target发送一次指定的selector消息, CADisplayLink类对应的selector就会被调用一次。所以通常情况下,按照iOS设备屏幕的刷新率60次/秒 - 延迟:
iOS设备的屏幕刷新频率是固定的,CADisplayLink在正常情况下会在每次刷新结束都被调用,精确度相当高。但如果调用的方法比较耗时,超过了屏幕刷新周期,就会导致跳过若干次回调调用机会。如果CPU过于繁忙,无法保证屏幕60次/秒的刷新率,就会导致跳过若干次调用回调方法的机会,跳过次数取决CPU的忙碌程度。 - 使用场景:
从原理上可以看出,CADisplayLink适合做界面的不停重绘,比如视频播放的时候需要不停地获取下一帧用于界面渲染。
4.重要属性
- frameInterval:
NSInteger类型的值,用来设置间隔多少帧调用一次selector方法,默认值是1,即每帧都调用一次。 - duration:
readOnly的CFTimeInterval值,表示两次屏幕刷新之间的时间间隔。需要注意的是,该属性在target的selector被首次调用以后才会被赋值。selector的调用间隔时间计算方式是:调用间隔时间 = duration × frameInterval。
三、GCD方式
执行一次
-
double delayInSeconds = 2.0;
-
dispatch_time_t popTime = dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, delayInSeconds * NSEC_PER_SEC);
-
dispatch_after(popTime, dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^(void){
-
//执行事件
-
});
重复执行
-
NSTimeInterval period = 1.0; // 设置时间间隔
-
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0);
-
dispatch_source_t _timer = dispatch_source_create(DISPATCH_SOURCE_TYPE_TIMER, 0, 0, queue);
-
dispatch_source_set_timer(_timer, dispatch_walltime(NULL, 0), period * NSEC_PER_SEC, 0); //每秒执行
-
dispatch_source_set_event_handler(_timer, ^{
-
//在这里执行事件
-
});
-
dispatch_resume(_timer);
[iOS] iPad与iPhone上各种标准控件的大小
iPhone和iPad下各种常见控件的宽度和标准是一样的,所以这里就用iPhone说明。
Sizes of iPhone UI Elements
Element Size (in points) Window (including status bar) 320 x 480 pts Status Bar
(How to hide the status bar)20 pts View inside window
(visible status bar)320 x 460 Navigation Bar 44 pts Nav Bar Image /
Toolbar Imageup to 20 x 20 pts (transparent PNG) Tab Bar 49 pts Tab Bar Icon up to 30 x 30 pts (transparent PNGs) Text Field 31 pts Height of a view inside
a navigation bar416 pts Height of a view inside
a tab bar411 pts Height of a view inside
a navbar and a tab bar367 pts Portrait Keyboard height 216 pts Landscape Keyboard height 140 pts Points vs. Pixels
The iPhone 4 introduced a high resolution display with twice the pixels of previous iPhones. However you don’t have to modify your code to support high-res displays; the coordinate system goes by points rather than pixels, and the dimensi***** in points of the screen and all UI elements remain the same.
iOS 4 supports high resolution displays (like the iPhone 4 display) via the scale property on UIScreen, UIView, UIImage, and CALayer classes. If the object is displaying high-res content, its scale property is set to 2.0. Otherwise it defaults to 1.0.
All you need to do to support high-res displays is to provide @2x versi***** of the images in your project. See the checklist for updating to iOS4 or Apple documentation for Supporting High Resolution Screens for more info.
Adjusting Sizes
Click here to see how to adjust View Frames and Bounds.
Additional References
Apple Documentation: Points vs. PixelsApple Documentation: UIBarButtonItem Class Reference says “Typically, the size of a toolbar and navigation bar image is 20 x 20 points.”
Apple Documentation: UITabBarItem Class Reference says “The size of an tab bar image is typically 30 x 30 points.”
iOS 11开发教程(十四)iOS11应用代码添加视图
如果开发者想要使用代码为主视图添加视图,该怎么办呢。以下将为开发者解决这一问题。要使用代码为主视图添加视图需要实现3个步骤。
(1)实例化视图对象
每一个视图都是一个特定的类。在Swift中,经常会说,类是一个抽象的概念,而非具体的事物,所以要将类进行实例化。实例化一个视图对象的具体语法如下:
let/var 对象名=视图类()
以我们接触的*个视图View为例,它的实例化对象如下:
let newView=UIView()
其中,UIView是空白视图的类,newView是UIView类实例化出来的一个对象。
(2)设置视图的位置和大小
每一个视图都是一个区域,所以需要为此区域设置位置和大小。设置位置和大小的属性为frame,其语法形式如下:
对象名.frame=CGRect(x ,y ,width,height)
其中,x和y表示视图在主视图中的位置,width和height表示视图的大小。以下为实例化的对象newView设置位置和大小:
newView.frame=CGRect(x: 67, y: 264, width: 240, height: 128)
其中,67和264表示此视图的主视图中的位置,240和128表示此视图的大小。
注意:步骤1和步骤2也可以进行合并。例如,以下的代码是将UIView类的实例化对象和设置位置大小进行了合并:
let newView=UIView(frame: CGRect(x: 67, y: 264, width: 240, height: 128))
(3)将视图添加到当前的视图中
*后,也是*为关键的一步,就是将实例化的对象添加到主视图中。这样才可以进行显示。此时需要使用到AddSubview()方法,其语法形式如下:
this.view.addSubview (视图对象名)
以下将实例化的对象newView添加到当前的主视图中,代码如下:
self.view.addSubview(newView)
【示例1-2】以下将使用代码为主视图添加一个View空白视图。代码如下:
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
let newView=UIView(frame: CGRect(x: 67, y: 264, width: 240, height: 128))
self.view.addSubview(newView)
}
……
}
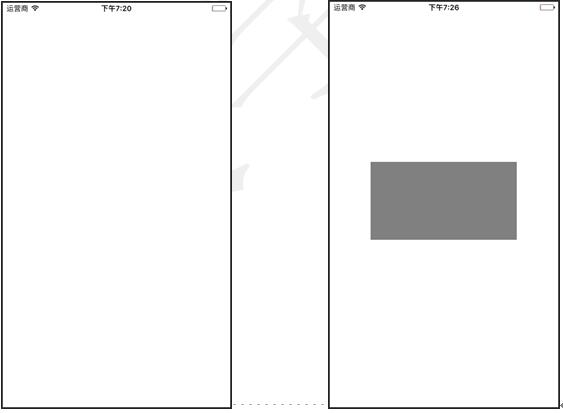
此时运行程序,会看到如图1.50所示的效果。在此运行效果中也是看不到添加的视图的。这是因为添加的视图默认是白色的背景,如果想要看到视图,需要设置它的背景。例如以下的代码,将背景颜色设置为了灰色:
newView.backgroundColor=UIColor.gray
此时运行程序,会看到如图1.51所示的效果。

苹果App Store简介
App store即application store,通常理解为应用商店。App store是苹果公司基于iPhone的软件应用商店,向iPhone的用户提供第三方的应用软件服务,这是苹果开创的一个让网络与手机相融合的新型经营模式。
2008年3月6日,苹果对外发布了针对iPhone的应用开发包(SDK),供免费下载,以便第三方应用开发人员开发针对iPhone及Touch的应用软件。不到一周时间,3月12日,苹果宣布已获得超过100,000次的下载,三个月后,这一数字上升至250,000次。苹果公司一直以来推出的产品在技术上都保持一定的封闭性,比如当年的Mac,此次推出SDK可以说是前所未有的开放之举。继 SDK推出之后,同年7月11日,苹果APP Store正式上线。7月14日,APP Store中可供下载的应用已达800个,下载量达到1千万次。2009年1月16日,数字刷新为,逾1.5万个应用,超过5亿次下载。APP Store平台上大部分应用价格低于10美元,并且有约20%的应用是供免费下载的。用户购买应用所支付的费用由苹果与应用开发商3:7分成。
App store模式的意义在于为第三方软件的提供者提供了方便而又高效的一个软件销售平台,使得第三方软件的提供者参与其中的积*性空前高涨,适应了手机用户们对个性化软件的需求,从而使得手机软件业开始进入了一个高速、良性发展的轨道,是苹果公司把App store这样的一个商业行为升华到了一个让人效仿的经营模式,苹果公司的App store开创了手机软件业发展的新篇章,App store无疑将会成为手机软件业发展史上的一个重要的里程碑,其意义已远远超越了“iPhone的软件应用商店”的本身。

